Featured Posts
NAS Backup: RAID and The 3-2-1 Strategy Explained
![]() Giorgio Zhang - Jul 03, 2025
Giorgio Zhang - Jul 03, 2025
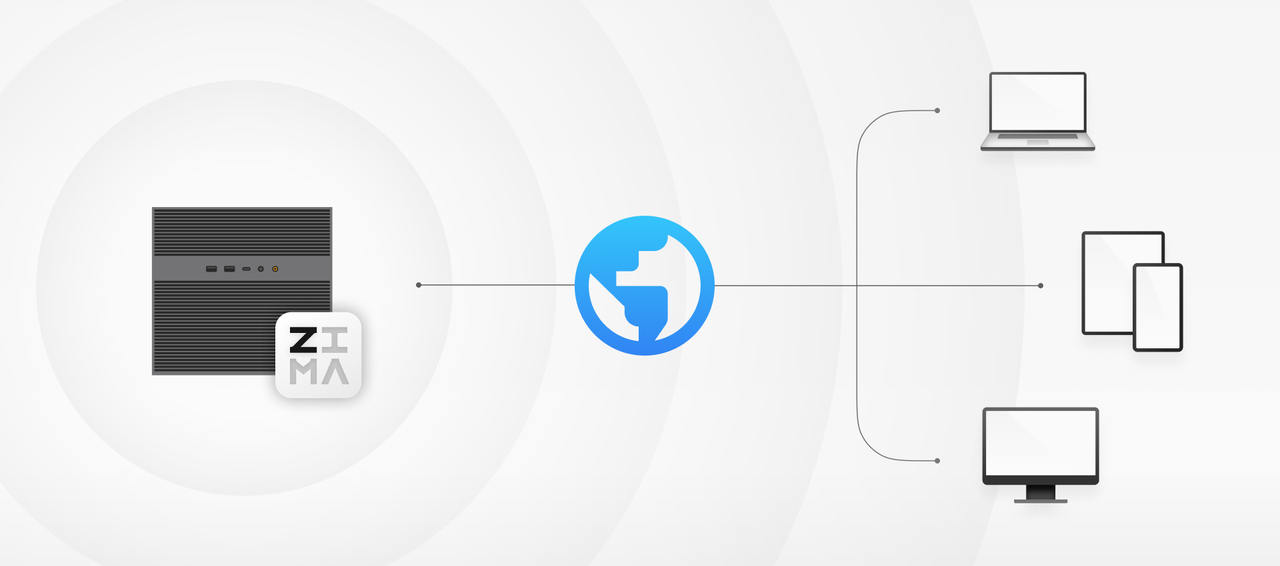

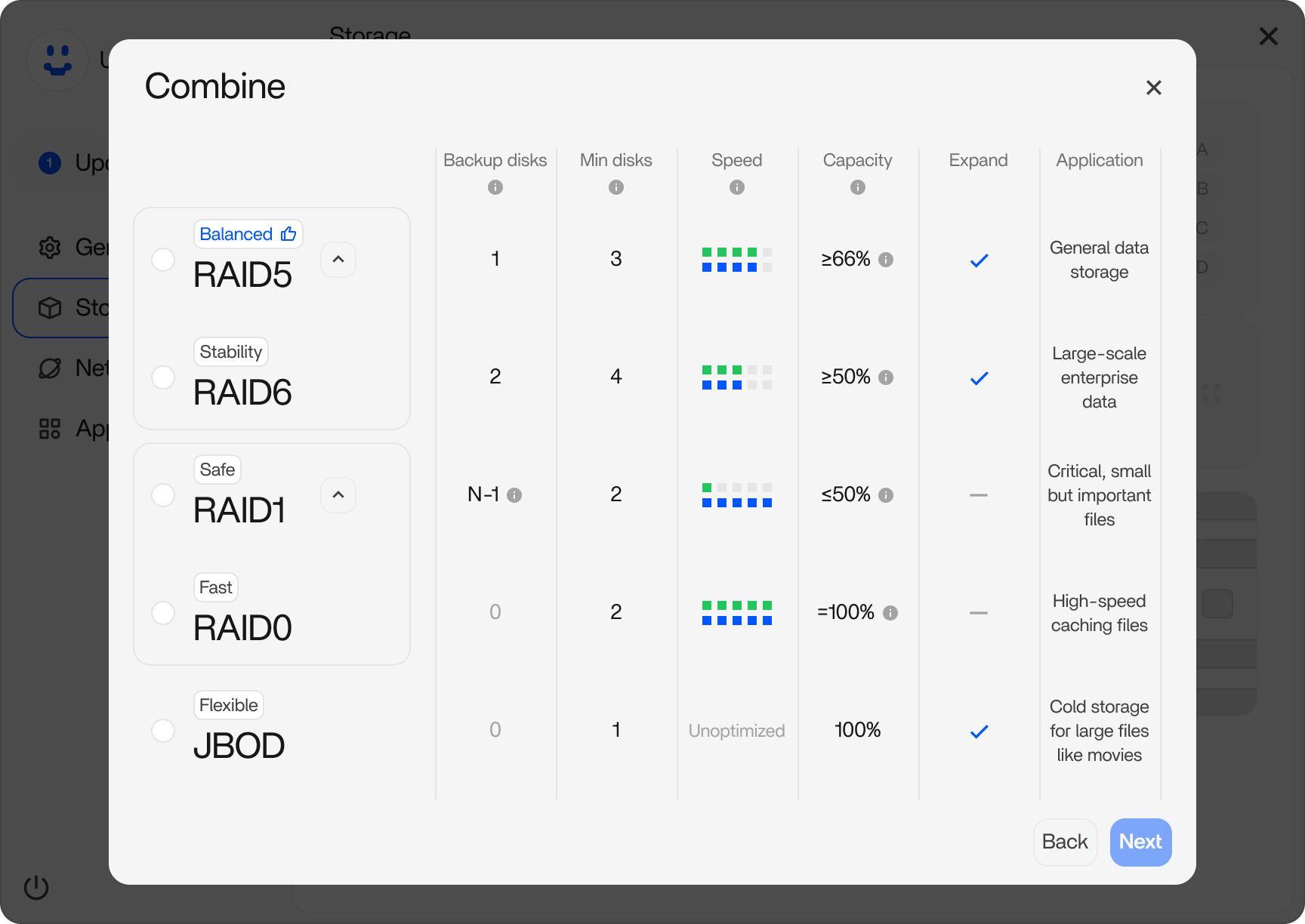
Part 1. Understanding RAID: Redundancy, Not a Backup

Part 2. The Gold Standard: The 3-2-1 Backup Strategy
- Have at least (3) copies of your data.
- Store these copies on (2) different types of media.
- Keep (1) copy off-site.
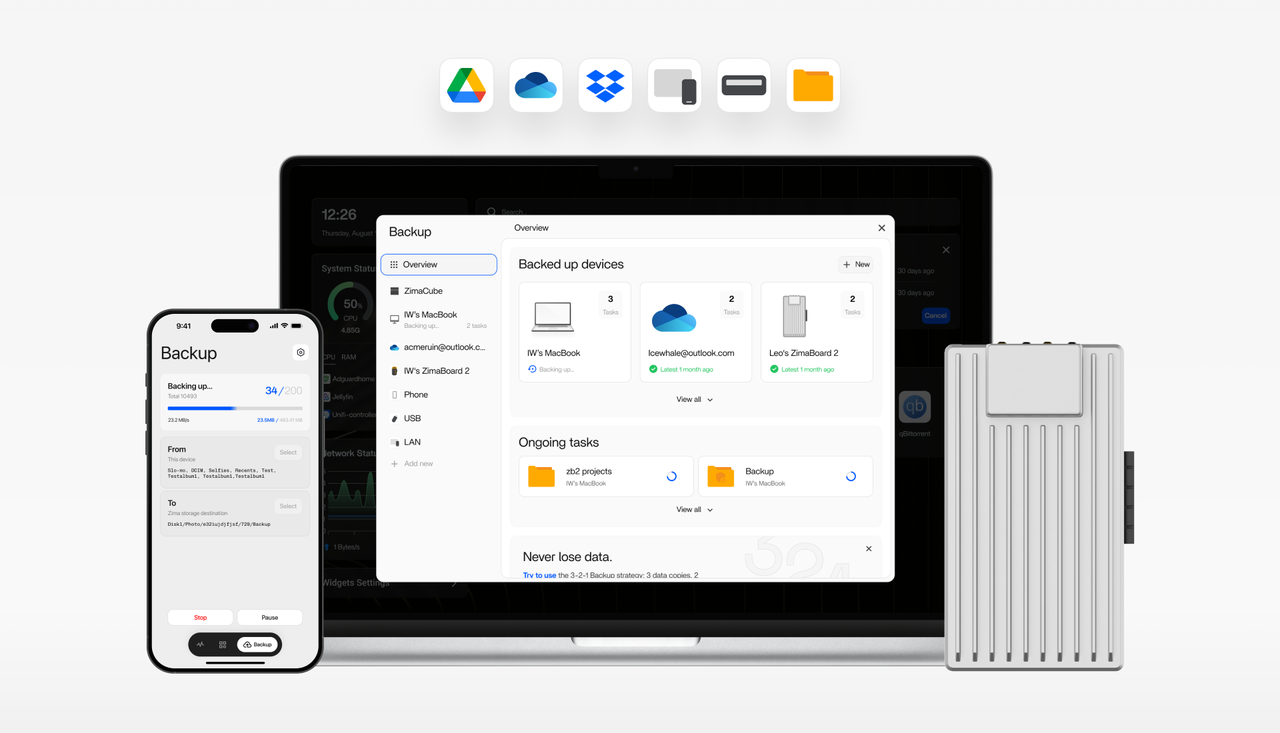
- Three Copies of Your Data: This includes your original data and at least two backups. If one or even two copies are compromised, you still have a version to restore from.
- Two Different Media: Storing your backups on different types of storage media protects you from failures related to a specific medium. For example, you could have your primary data on your NAS (which itself might use hard drives in a RAID configuration) and a backup on an external hard drive.
- One Off-site Copy: This is the cornerstone of disaster recovery. If a local event like a fire, flood, or theft compromises both your primary data and your local backup, the off-site copy remains safe. This could be a physical drive stored at a different location or, more conveniently, a cloud backup.
Part 3. Implementing the 3-2-1 Rule with Your Zima NAS

- External USB Drive: The simplest method for a local backup is to connect an external USB hard drive to your ZimaCube. ZimaOS allows for easy file management and you can use built-in tools or applications from the App Store to schedule regular backups to the connected drive.
- Another NAS or Computer: You can also back up your Zima device to another computer or Zima NAS through network. Tools like Syncthing can be used to synchronize files between your Zima device and other computers, creating another layer of data distribution.
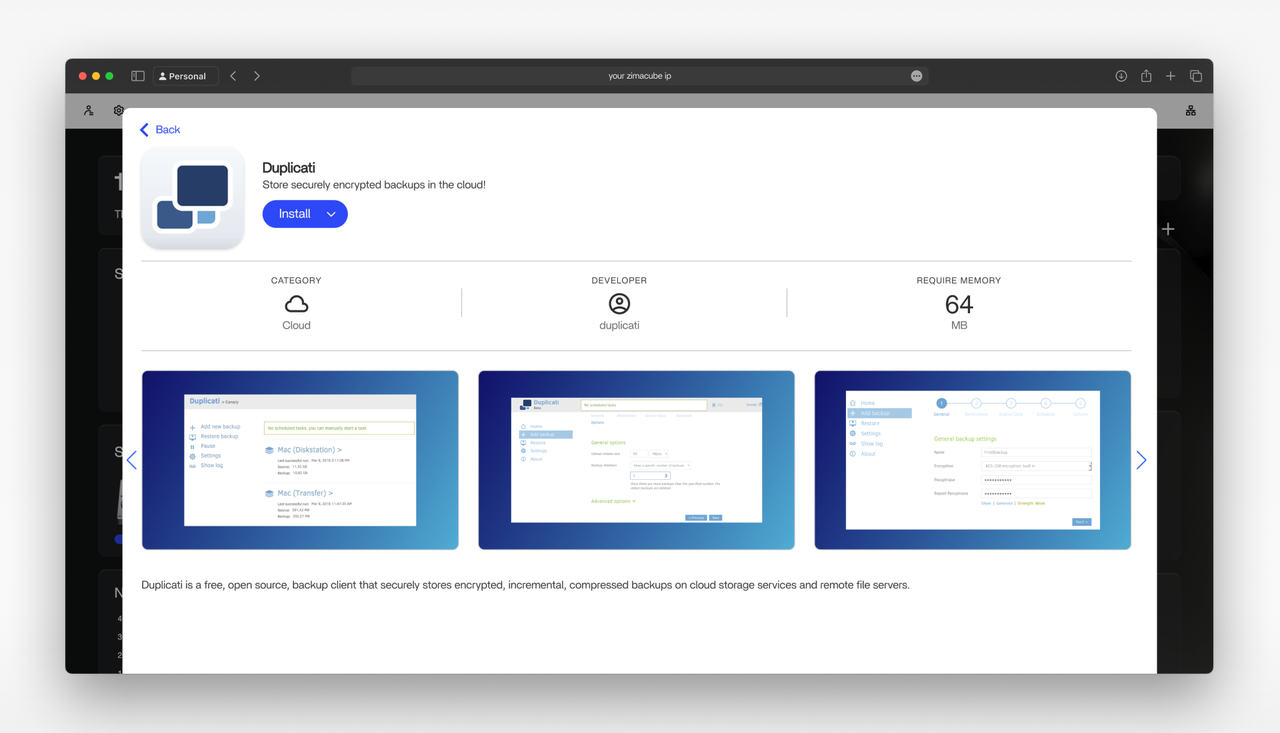
- Cloud Storage Integration: ZimaOS offers an App Store where you can find various backup applications. Applications like Duplicati can provide more advanced backup features, including encryption and scheduling to multiple destinations. By syncing your critical data to a cloud service, you create a secure off-site backup that is accessible from anywhere. Services like Backblaze B2, IDrive, and others offer S3-compatible storage that can be integrated with NAS backup tools.
- Physical Off-site Backup: For a more hands-on approach, you can maintain a second external hard drive that you regularly update and store at a different physical location, such as a friend’s house or a safe deposit box.
Conclusion


Your friendly guide to the world of NAS! We’re all about cutting through the tech jargon to bring you the most useful and practical software and hardware knowledge. Whether you’re looking to build your first home server, create a rock-solid backup system, or set up a personal media library, we break down the concepts step-by-step. Let’s explore DIY builds, compare off-the-shelf options, and master apps together to help you get the most out of your network storage.