Reviews
ODROID Review: Good Raspberry Pi Alternative
![]() John Guan - Apr 07, 2023
John Guan - Apr 07, 2023
ODROID is a line of single-board computers (SBCs) that are known for their high performance and versatility. These devices are designed to provide a powerful computing platform for a wide range of applications, including gaming, media centers, robotics, and more. In this article, we will explore what ODROID is, its key features, and how it compares to the popular Raspberry Pi SBC.
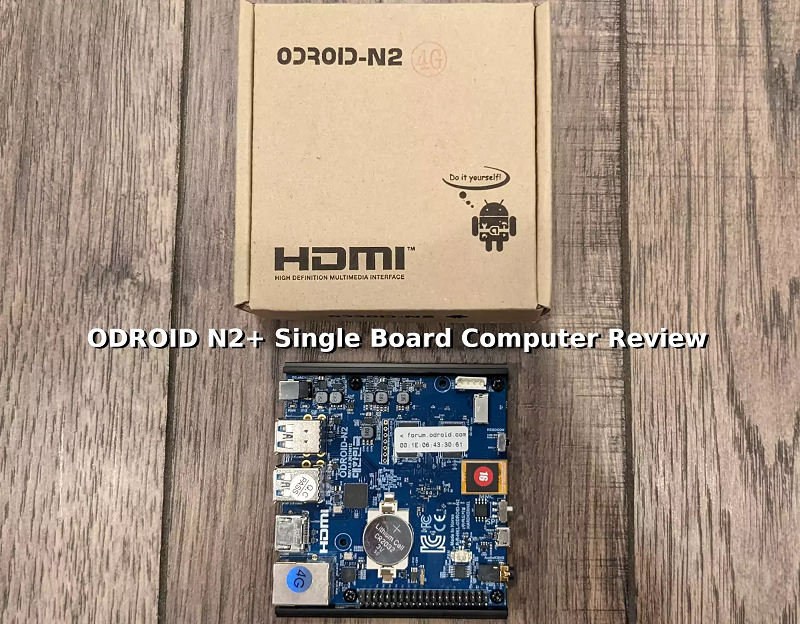
Part 1: What is ODROID?
Part 2: What are ODROID’s Pros and Cons?
Part 3: What you should know about ODROID?
Part 4: Alternative ODROID – ZimaBoard Single Board Server
Part 5: FAQs about ODROID
Part 1: What is ODROID?
ODROID is a series of SBCs that are produced by Hardkernel, a South Korean company. These devices are designed to be highly flexible and powerful, with a range of hardware and software options that make them suitable for a wide range of applications. ODROID boards are known for their high-performance specifications, including powerful CPUs, large amounts of RAM, and fast storage options.
One of the key advantages of ODROID boards is their flexibility. These devices can run a range of operating systems, including Android, Ubuntu, and other Linux distributions. This makes them highly versatile and suitable for a wide range of applications, including gaming, media centers, servers, and more.
Is ODROID better than Raspberry Pi?
While the Raspberry Pi is one of the most popular SBCs on the market, it is not necessarily the most powerful or versatile. ODROID devices offer a range of advantages over the Raspberry Pi, including:
High-performance specifications: ODROID devices typically feature more powerful CPUs, larger amounts of RAM, and faster storage options than the Raspberry Pi.
More hardware options: ODROID devices often offer more hardware options than the Raspberry Pi, including support for eMMC modules, more USB ports, and more.
More software options: ODROID devices can run a wider range of operating systems and software than the Raspberry Pi, including Android and other Linux distributions.
Better graphics capabilities: Some ODROID devices feature more powerful graphics capabilities than the Raspberry Pi, which can be an advantage for gaming and media center applications.
Overall, while the Raspberry Pi is a popular and versatile device, the ODROID offers a range of advantages that make it a more powerful and flexible option for many applications.
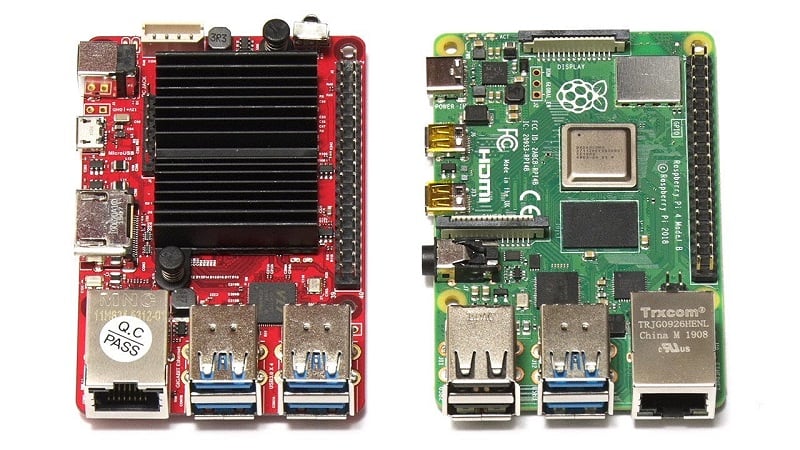
Part 2: What are ODROID’s Pros and Cons?
ODROID is a single-board computer that has been gaining popularity in recent years due to its powerful hardware and versatile software capabilities. Here are some of the pros and cons of using an ODROID:
Pros:
Powerful hardware: ODROID devices are known for their impressive hardware specs, which include high-performance CPUs, GPUs, and large amounts of RAM. This makes them ideal for tasks that require a lot of processing power, such as gaming, media streaming, and server hosting.
Versatile software: ODROID devices are compatible with a wide range of operating systems, including Android, Linux, and Windows. They can also run a variety of software applications, making them suitable for a wide range of use cases.
Expandable: Many ODROID devices come with built-in expansion ports, which allow users to add additional hardware components such as cameras, microphones, and sensors. This makes ODROID devices highly versatile and customizable.
Cost-effective: Despite their powerful hardware specs, ODROID devices are often more affordable than other high-end single-board computers.
Cons:
Steep learning curve: ODROID devices can be more difficult to set up and configure than other single-board computers. Users may need to have a more in-depth understanding of hardware and software to get the most out of their ODROID device.
Limited support: Unlike more popular single-board computers like the Raspberry Pi, ODROID devices may have limited community support. This can make it more difficult to find help or troubleshooting resources if something goes wrong.
Power consumption: Due to their high-performance hardware, ODROID devices may consume more power than other single-board computers. This can be a consideration for users who want to minimize their energy usage.
Limited availability: ODROID devices are not as widely available as other single-board computers, which can make them more difficult to purchase in some regions.
ODROID devices offer powerful hardware and versatile software capabilities, making them a great choice for users who need a high-performance single-board computer. However, their steep learning curve and limited support may make them less suitable for beginners or users who are looking for a more user-friendly device.
Part 3: What you should know about ODROID?
ODROID is a series of single-board computers manufactured by Hardkernel, a South Korean company. ODROID is known for its high performance, compact size, and versatility. It is a popular choice among tech enthusiasts, hobbyists, and developers.

What is ODROID used for?
ODROID is primarily used for DIY projects, home automation, gaming, and media center applications. With its high processing power, it is also used for software development and other applications that require heavy computing.
Does RetroPie work on ODROID?
Yes, RetroPie works on ODROID. RetroPie is a popular retro-gaming platform that allows users to play classic games on modern hardware. ODROID is one of the compatible hardware platforms for RetroPie.
ODROID Hardware
ODROID comes in various models, each with different hardware specifications. The latest models include the ODROID-N2+, ODROID-HC4, and ODROID-GO Super.
ODROID Specifications
The ODROID-N2+ is a powerful single-board computer equipped with a quad-core Cortex-A73 CPU and a dual-core Cortex-A53 CPU. It also has 2GB or 4GB DDR4 RAM, Gigabit Ethernet, and HDMI 2.0 output. It can support up to 4K resolution and runs on the latest Android or Linux operating systems.
The ODROID-HC4 is designed for network-attached storage (NAS) applications. It is powered by a quad-core Cortex-A55 CPU, 4GB DDR4 RAM, and two SATA ports for up to 32TB of storage. It also has Gigabit Ethernet and USB 3.0 ports.
The ODROID-GO Super is a handheld gaming console that features a 3.5-inch IPS screen, WiFi connectivity, and a 4000mAh battery. It runs on the ODROID-GO firmware, which is an open-source project that allows users to play classic games.
How does ODROID perform?
ODROID is known for its high performance, thanks to its powerful hardware specifications. Its quad-core CPU and high-speed RAM allow for smooth and fast performance. It also has excellent graphics capabilities and supports 4K video playback. ODROID is an excellent choice for gaming, media center applications, and other resource-intensive tasks.
However, ODROID’s high performance comes at a cost. It requires more power than other single-board computers, which can lead to increased power consumption and higher operating temperatures.
Part 4: Alternative ODROID – ZimaBoard Single Board Server
While ODROID has been a popular choice for single-board computers, there are also other options available on the market, one of which is the ZimaBoard Single Board Server. In this section, we’ll explore the key features, pros, and cons of the ZimaBoard as an alternative to the ODROID.
The ZimaBoard is a powerful single-board server that comes with a range of features designed to enhance performance, usability, and versatility.

Check the Pros and Cons of the ZimaBoard below.
Pros:
High Performance: The ZimaBoard offers powerful performance that is comparable to many high-end desktops and servers, making it ideal for running demanding workloads.
Expandable Storage: With support for up to two NVMe SSDs and a microSD card slot, the ZimaBoard offers plenty of storage options for users.
Gigabit Ethernet and WiFi: The ZimaBoard comes with built-in Gigabit Ethernet and WiFi capabilities, providing fast and reliable network connectivity.
Multiple Operating Systems: The ZimaBoard supports various operating systems, including Ubuntu, Debian, and OpenMediaVault, making it highly versatile and suitable for a range of use cases.
Developer-Friendly: The ZimaBoard comes with a range of developer-friendly features, such as a UART connector, SPI header, and GPIO pins, making it easy to customize and develop new applications.
Cons:
Availability: The ZimaBoard may be less widely available than some other single-board computers, making it harder to purchase in some regions.
Limited Community Support: Compared to more popular single-board computers, such as Raspberry Pi and ODROID, the ZimaBoard has a smaller user community, which may limit the availability of support and resources.
What you can do with ZimaBoard?
ZimaBoard is a single-board server that is capable of performing a wide range of functions, making it a versatile and powerful device for a variety of applications. Here are some of the things that you can do with ZimaBoard:
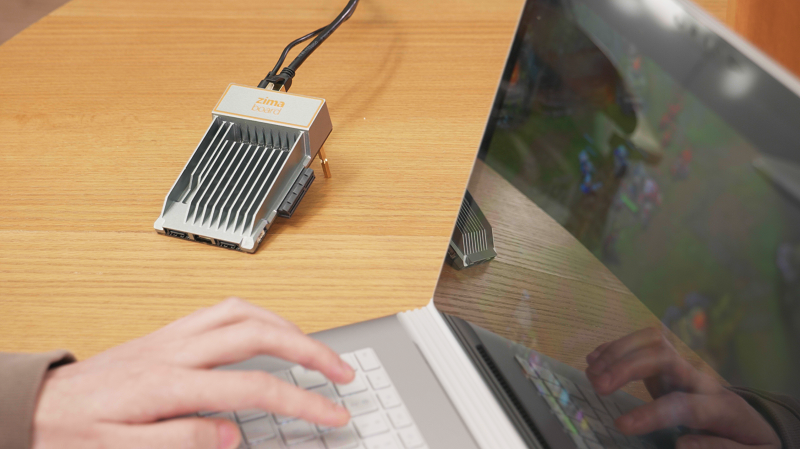

Run a web server: ZimaBoard is a great platform for hosting web applications and websites. It is capable of running popular web servers software like Apache, Nginx, and Lighttpd, and can handle multiple concurrent connections without breaking a sweat.
Create a media server: If you have a large collection of music, movies, and TV shows, ZimaBoard can be used to create a media server that can stream content to other devices on your network. With the right software, you can even access your media remotely over the internet.
Host game servers: ZimaBoard is also a great platform for hosting game servers. Whether you want to host a Minecraft server or run your own game server for a popular title like Counter-Strike: Global Offensive or Team Fortress 2, ZimaBoard can handle the load.
Run a VPN: If you’re concerned about your online privacy and security, you can use ZimaBoard to run a virtual private network (VPN). With a VPN, you can encrypt your internet traffic and keep your browsing data private from prying eyes.
Build a home automation system: ZimaBoard can also be used to build a home automation system. By connecting sensors and other devices to ZimaBoard, you can automate tasks like turning on lights, adjusting your thermostat, and even watering your plants.
Set up a file server: If you need to share files between devices on your network, ZimaBoard can be used to set up a file server. You can use a variety of software packages to create a file server that is accessible from any device on your network.
Develop software: ZimaBoard is also a great platform for software development. You can use it to develop and test software for a variety of platforms, including Linux, Android, and more.
Run a database server: If you need to store and manage large amounts of data, ZimaBoard can be used to run a database server. With a variety of database management systems available for Linux, you can create a powerful database server that can handle a large amount of data.
How to set up ZimaBoard Single Board Server?
To set up the ZimaBoard Single Board Server, you will need to follow the steps below:
Assemble the board: The ZimaBoard Single Board Server comes with a bare board and accessories, including a metal enclosure, screws, and standoffs. You will need to assemble the board by attaching the screws and standoffs to the board and placing it in the enclosure.
Connect peripherals: After assembling the board, you will need to connect peripherals such as a monitor, keyboard, and mouse to the board’s available ports. The ZimaBoard Single Board Server has a range of ports, including USB 3.0, Ethernet, HDMI, and SATA.
Install the operating system: Once the peripherals are connected, you will need to install an operating system on the ZimaBoard Single Board Server. The board supports a range of operating systems, including Ubuntu, Debian, and OpenWrt.
Configure the board: After installing the operating system, you will need to configure the ZimaBoard Single Board Server for your specific use case. This includes setting up network configurations, installing software, and creating user accounts.
Part 5: FAQs about ODROID
ODROID is a versatile and powerful single-board computer that has become a popular choice for DIY enthusiasts and developers alike. As with any technology, there are bound to be questions and concerns regarding its use. In this section, we will address some of the most common questions regarding ODROID.
Which ODROID is best?
The answer to this question depends on your specific needs and use case. Each ODROID model has its own strengths and weaknesses, so it’s important to consider what you’ll be using the board for before making a decision. For example, if you need a lot of processing power and want to use the latest software, the ODROID-XU4 may be your best bet. On the other hand, if you’re looking for a more budget-friendly option with moderate performance, the ODROID-C2 may be the better choice.
How do I add ROMs to ODROID?
To add ROMs to your ODROID, you’ll first need to install an emulator. There are a variety of emulators available for ODROID, including RetroPie, which is a popular choice for retro gaming enthusiasts. Once you have the emulator installed, you can add ROMs by connecting your ODROID to your computer via USB and transferring the ROMs to the appropriate folder on the board. The process may vary slightly depending on the specific emulator you’re using.
How much power does ODROID M1 use?
The ODROID M1 uses about 2 watts of power when idle and up to 5 watts under full load. This makes it a relatively energy-efficient option compared to other single-board computers on the market.
What can you do with ODROID C2?
The ODROID C2 is a powerful board that can be used for a variety of applications, including a media center, gaming console, and even as a small desktop computer. With its quad-core CPU and 2GB of RAM, the ODROID C2 is capable of running a variety of software, including Android, Linux, and even Windows 10.
How much memory does the ODROID-XU4 have?
The ODROID-XU4 comes with 2GB of DDR3 RAM, which is more than enough for most applications. However, it’s worth noting that the board does not support ECC memory, which may be a concern for some users.
Conclusion:
ODROID is a powerful and versatile single-board computer that can be used for a variety of applications. Whether you’re a DIY enthusiast, a developer, or just someone looking for a budget-friendly computer, there is likely an ODROID model that will suit your needs. By understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each model and considering your specific use case, you can make an informed decision and get the most out of your ODROID board.


